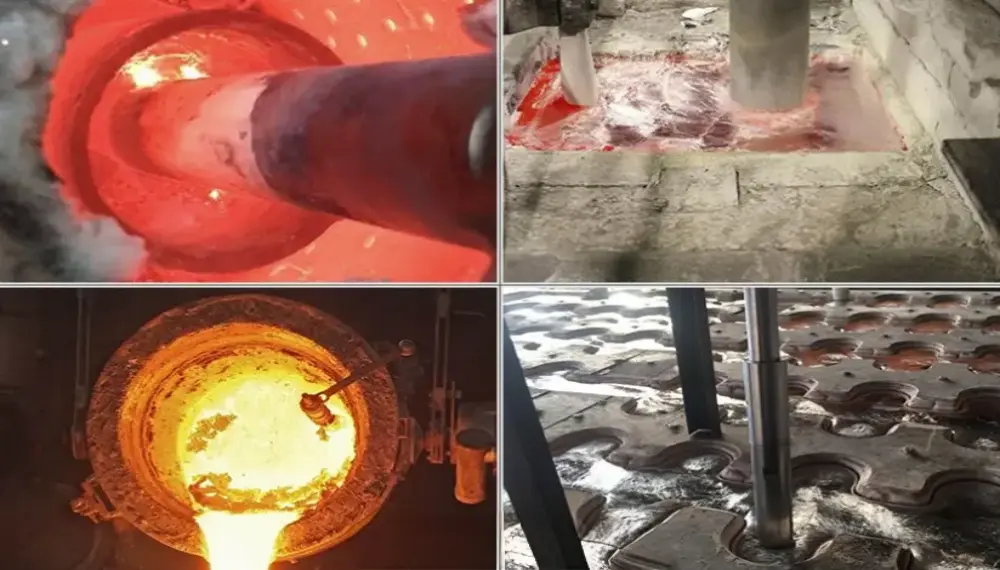
Ultrasonic waves help improve the quality of metal powders
1. Ultrasonic atomization powder making technology
1. Technical principle
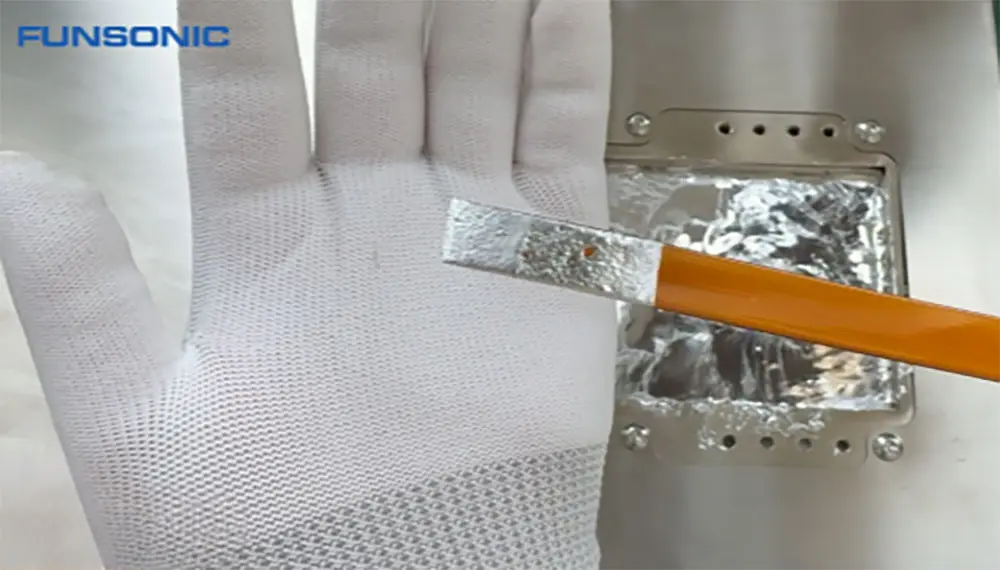
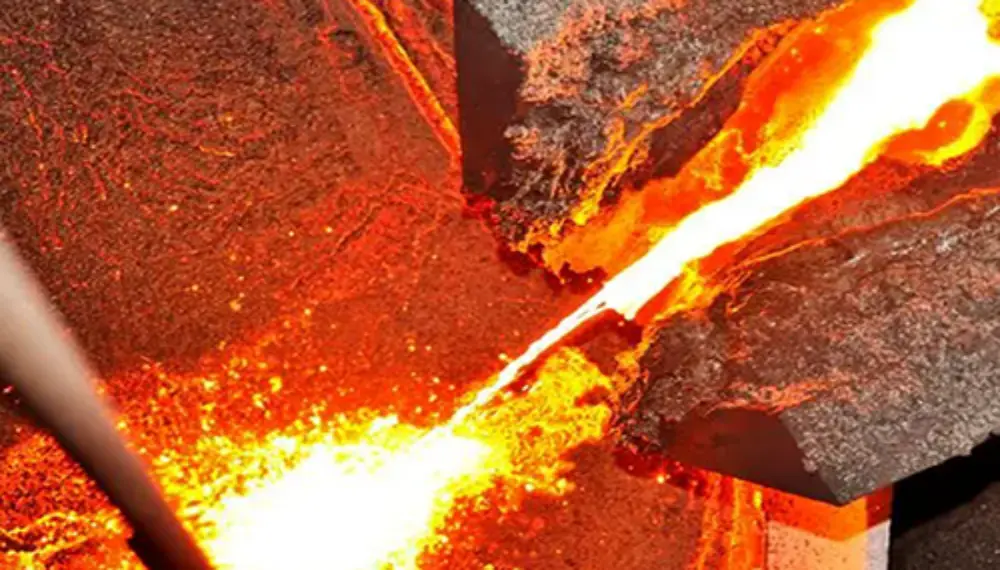
Ultrasonic atomization powder making technology can be divided into contact atomization and non-contact atomization. With the help of high-frequency sound wave vibration energy, the metal liquid flow is accurately broken and dispersed into fine mist droplets, and then solidified into powder in a specific cooling environment. The contact atomization currently used is suitable for metal materials with low melting points (≦1000℃), such as magnesium, aluminum, tin, silver, indium, lead, etc.
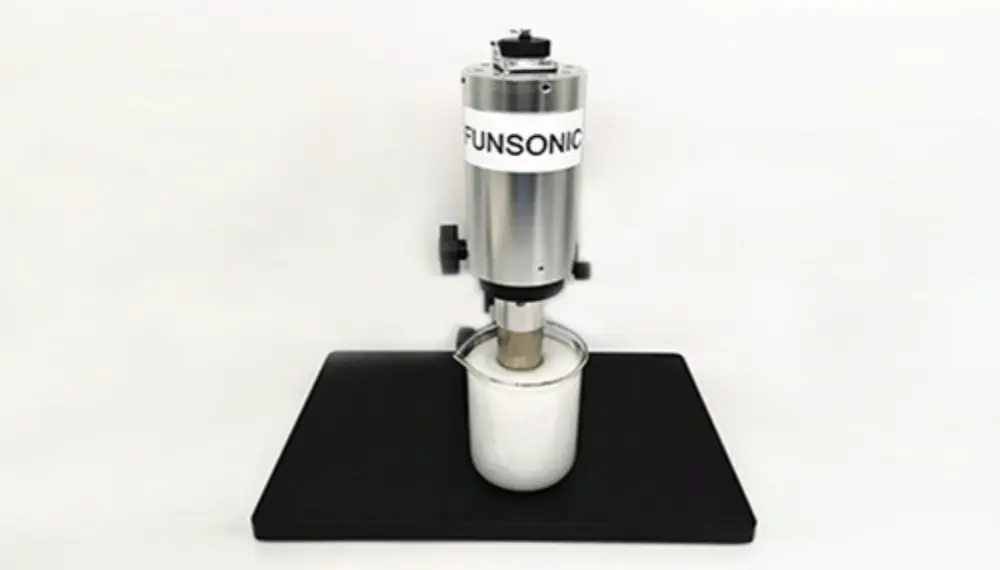
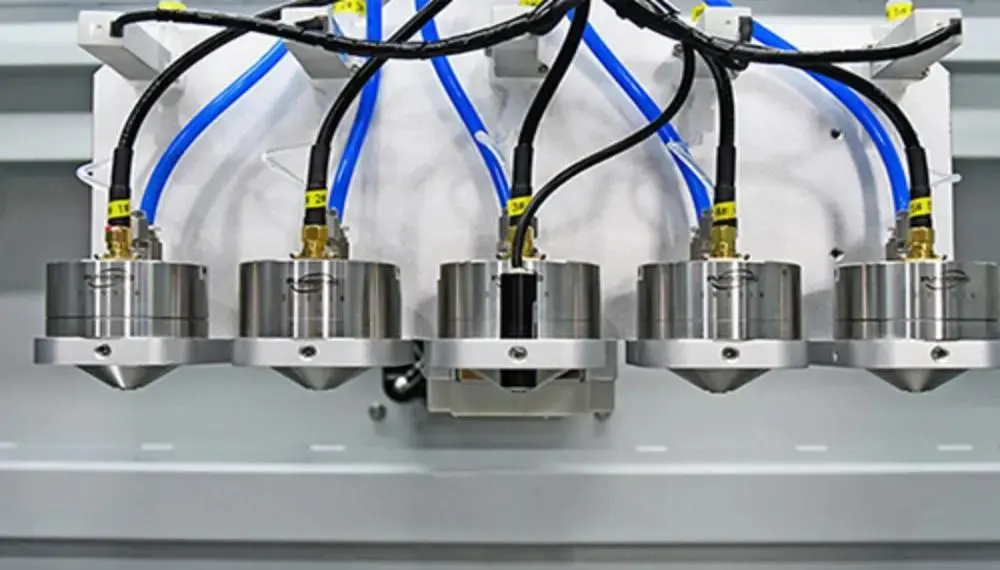
2. Equipment structure
The core module includes a metal smelting furnace, an atomization tank, an ultrasonic metal atomization treatment system, an inert gas generator, etc.; the powder particle size and output are controlled by adjusting the flow rate of the liquid and adjusting the power of the ultrasonic wave.
3. Technological breakthrough
FUNSONIC combines ultrasonic application with traditional metal powder making methods to develop ultrasonic metal atomization technology. Through automated production equipment, it achieves the purpose of mass production of low-melting-point metal powder materials and can effectively control the uniformity and particle size of metal powders.
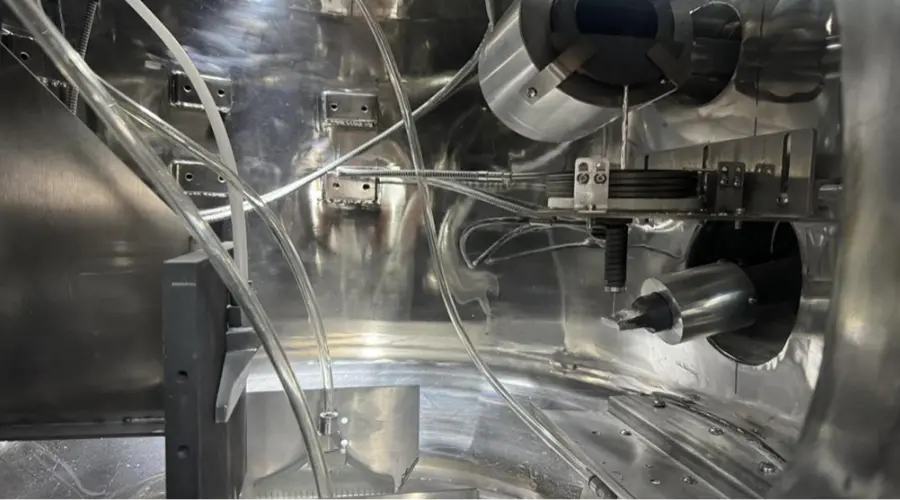

2. Ultrasonic-assisted metal powder processing technology
1. Dispersion and mixing optimization
Use ultrasonic high-frequency vibration and cavitation effect to break up the metal solution dripping on the ultrasonic tool head, so that the solution is evenly dispersed in atomized particles, and the gas in the liquid is precipitated without adhesion, so as to achieve the consistency of powder dispersion and formed particles.
2. Particle size control and screening
The atomized and solidified particles can be screened with high precision through the ultrasonic vibrating screen device to obtain powder with consistent particle size.
3. Technological breakthroughs and application prospects
1. 3D printing and additive manufacturing
Ultrasonic atomization powder making technology is used to prepare ultrafine metal powders with high sphericity and low oxygen content. It can meet the stringent requirements of additive manufacturing for powder fluidity and density, such as application in precision manufacturing fields such as special coatings and medical devices.
2. Powder metallurgy
Iron-based and copper-based alloy powders produced by ultrasonic atomization technology can be directly used in powder metallurgy processes to manufacture high-strength gears, wear-resistant bearings and other components, and optimize the porosity and material uniformity of traditional processes.
3. Electronics and Semiconductors
Ultrasonic powder making technology is used to control the nano-particle size of conductive materials such as high-purity copper powder and silver powder, which are applied to integrated circuit conductive paste, electronic packaging and other scenarios to improve the conductivity and reliability of devices.
4. Energy and Chemical Industry
Battery Materials: Nano-scale nickel powder and cobalt powder prepared with the assistance of ultrasound are used as positive electrode materials for lithium batteries to improve energy density and cycle stability;
Catalyst: Ultrafine metal powders such as iron and cobalt are used as active components of industrial catalysts to accelerate the efficiency of chemical reactions.
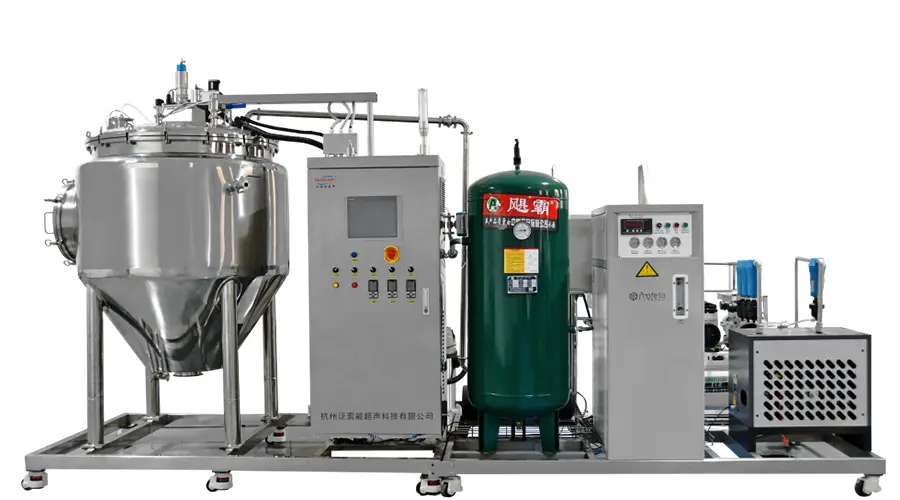

5. Aerospace and Military Industry
Non-contact ultrasonic powder making technology can produce high-melting-point alloy powders (such as tungsten carbide and titanium alloy) for spray repair or direct molding of high-temperature parts such as rocket nozzles and aircraft engine blades.
6. Biomedicine
Medical titanium alloy and magnesium alloy powders are prepared by ultrasonic atomization technology and used for bone implants or 3D printed customized prostheses, with both biocompatibility and mechanical properties.
4. Development Trend
At present, ultrasonic powder making technology still faces challenges such as high R&D cost investment of high melting point atomization equipment, in-depth development of industrial application fields, and low finished product output. In the future, it is necessary to further strengthen cooperation with relevant advanced manufacturing companies and scientific research institutes, form consensus and project planning, and make breakthroughs in key technologies such as ultrasonic metal atomization technology for preparing different metal powder materials.